Updated February 2025: Stop getting error messages and slow down your system with our optimization tool. Get it now at this link
- Download and install the repair tool here.
- Let it scan your computer.
- The tool will then repair your computer.
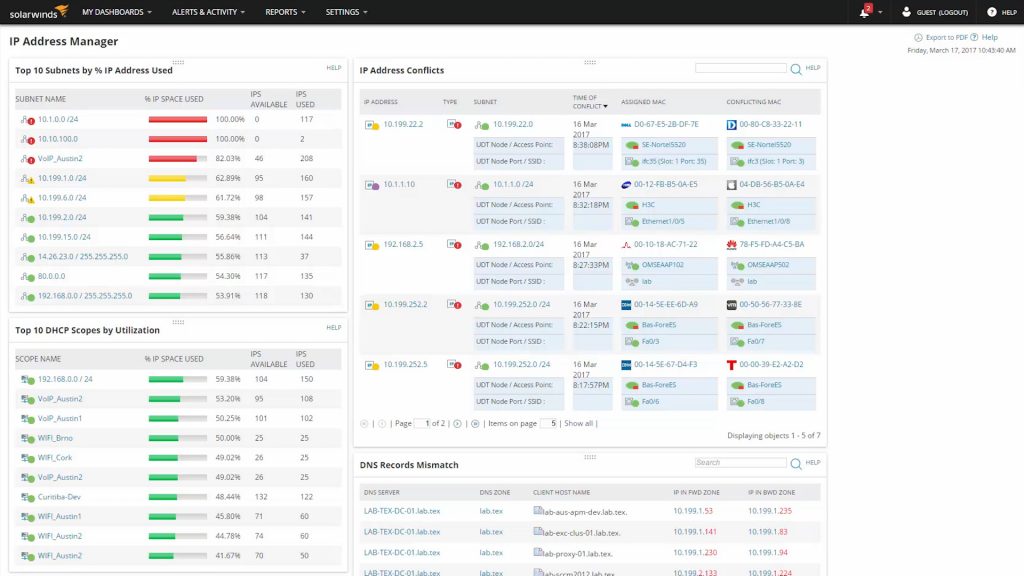
IP Address Management (IPAM) is an integrated suite of tools that enables end-to-end planning, provisioning, management and monitoring of your IP address infrastructure with a complete user experience. IPAM automatically detects the IP address infrastructure servers and Domain Name System (DNS) servers on your network and allows you to manage them from a central interface.
What is DHCP?
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and is a protocol used to assign IP addresses to devices. It is important to note the word “protocol” because it gives an indication of what it does: it is a process rule for assigning IP addresses, and it works the same way for any device or network. It also keeps track of all IP addresses on your network and any subnets that require IP addresses.
There are two main types of computers that are relevant to DHCP. Firstly, individual computers called hosts are what you think of when you consider using work computers, your own laptop, etc. The second type of computer is a server that can process and send data to other computers.
DHCP servers are those that have multiple IP addresses stored and ready to be assigned to hosts when they join the network. Another important part of the DHCP name that you need to understand is the word “Dynamic”. Dynamic in this context means that IP addresses are assigned “on demand” or dynamically when a computer requests an IP address from the pool of IP addresses stored on the DHCP server. By default, DHCP servers assign IP addresses for five days, meaning that a new IP address is assigned after that time. This process is automatic.
DHCP servers are capable of assigning IPv4 addresses to clients on your network. Another type of server, called a RADVD server or DHCPv6 server, can assign IPv6 addresses.
February 2025 Update:
You can now prevent PC problems by using this tool, such as protecting you against file loss and malware. Additionally, it is a great way to optimize your computer for maximum performance. The program fixes common errors that might occur on Windows systems with ease - no need for hours of troubleshooting when you have the perfect solution at your fingertips:
- Step 1 : Download PC Repair & Optimizer Tool (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista – Microsoft Gold Certified).
- Step 2 : Click “Start Scan” to find Windows registry issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Step 3 : Click “Repair All” to fix all issues.
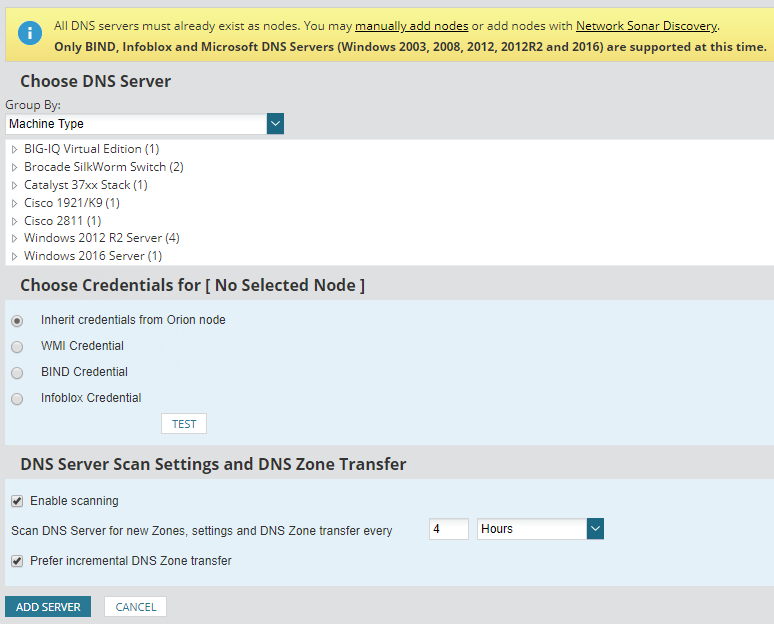
Adding a DNS server
All DNS servers must already exist as nodes in your installation before they can be added to the IPAM.
- Go to My Dashboard > DHCP and DNS Management
- Click the DNS Servers tab to display the current list of DNS servers.
- Click Add New > DNS Servers.
- Select a DNS server from the list. If the server is not displayed, use the Group by menu to sort the listed DNS servers.
- Select the server access details. WMI credentials can be inherited from the node to the DNS server.
- Click Test to confirm.
- If you provide Windows credentials to access and receive information via WMI, you must specify the account name in the following order: Domain or computer name [User name for domain-level authentication or user name for workgroup-level authentication].
- Select Enable Scanning to enable incremental DNS zone forwarding. The IPAM searches the DNS server for new zones and settings based on the time interval.
- Click Add Server. The DNS zones are displayed.
Adding a DNS Zone
If you have a DNS server with a DNS zone and the server has authority over the zone, you can also add the DNS zone to the IPAM. A single DNS server can have authority over multiple DNS zones. Three types of DNS zones are supported by the IPAM, namely the primary zone, the secondary zone, and the buffer zone.
Follow the instructions below to add a zone:
- From the Orion Web console, go to My Dashboards > IP Addresses > DHCP and DNS Management.
- Go to the DNS Zones tab. Now click the Add New button and then select DNS Zone from the drop-down list.
- On the Select DNS server page, select the DNS server to which the zone will be applied from the drop-down list and click Next.
- Then select the zone type. If you select the primary zone, you can register the zone in Active Directory if the DNS server is a domain controller, if you wish. For secondary and stub zones, you must specify a master DNS server.
- Then select the DNS search type. If you choose the advanced search, you must specify a DNS name for the zone. If you choose the reverse lookup, you must specify the network IP or zone name for the reverse lookup. Then click Next.
- Specify a name for the zone file, or just use the default name. This is where the DNS zone data is stored on the DNS server computer.
- You can both allow zone transfers and specify an interval for the transfer. Zone transfers are primarily used to synchronize subzones and buffer zones with the master DNS server.
- You can also choose to enable incremental zone transfers, which make only the changes necessary to synchronize with the source.
- Then click the Next button.
- Finally, check the information you have provided and make sure that everything is OK. Then click on the “Create a zone” button. Click OK when the confirmation dialog box appears.
https://documentation.solarwinds.com/en/success_center/ipam/Content/IPAM-DNS-management.htm
Expert Tip: This repair tool scans the repositories and replaces corrupt or missing files if none of these methods have worked. It works well in most cases where the problem is due to system corruption. This tool will also optimize your system to maximize performance. It can be downloaded by Clicking Here
