Updated February 2025: Stop getting error messages and slow down your system with our optimization tool. Get it now at this link
- Download and install the repair tool here.
- Let it scan your computer.
- The tool will then repair your computer.
The more complex the tasks you perform on your PC, the hotter your CPU will be. This is especially noticeable when playing games or editing heavy videos. However, your CPU may be prone to overheating anyway if it’s poorly ventilated or if the CPU’s thermal paste is worn out. Fortunately, there is a bit of a wonderful tool that you can use to reduce high temperatures and power consumption with a process called “undervolting”.
What is Undervolting?
Before you start, you have to ask yourself what exactly is on.
In most cases, the factory settings on processors are designed to put more voltage on the CPU than it really needs. Excessive voltage and current causes the CPU to heat up, which further reduces the performance of the CPU.
To solve this problem, reduced voltage is used. This is a simple process in which users use special tools such as Throttlestop or Intel XTU to lower the CPU voltage while maintaining overall performance.
While lowering the voltage won’t necessarily damage your processor, if you go overboard, you can make your computer unstable. On the other hand, a voltage spike can potentially damage your processor. However, if you use it wisely, you can overclock your processor.
Underclocking reduces the voltage/power sent to your processor. The more power your processor gets, the more it heats up. The less power it gets, the cooler it gets.
The special thing about voltage is that it doesn’t affect overall performance, even during intense gaming sessions.
February 2025 Update:
You can now prevent PC problems by using this tool, such as protecting you against file loss and malware. Additionally, it is a great way to optimize your computer for maximum performance. The program fixes common errors that might occur on Windows systems with ease - no need for hours of troubleshooting when you have the perfect solution at your fingertips:
- Step 1 : Download PC Repair & Optimizer Tool (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista – Microsoft Gold Certified).
- Step 2 : Click “Start Scan” to find Windows registry issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Step 3 : Click “Repair All” to fix all issues.
How to undervolt a CPU
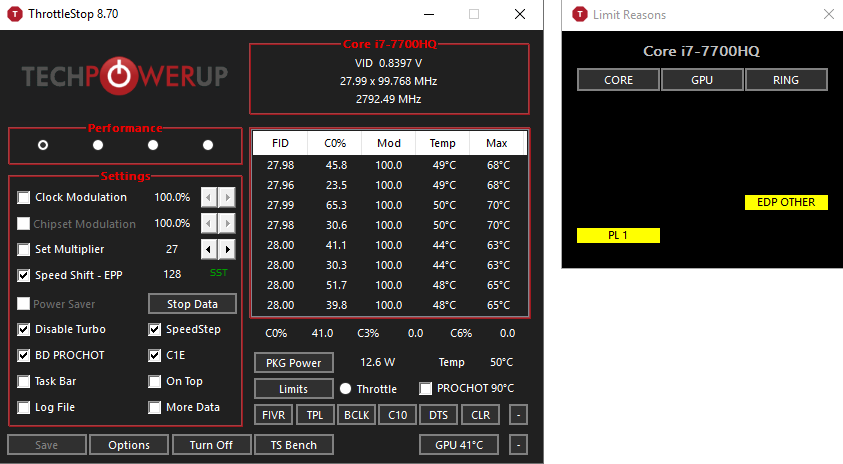
- First, to do this, we need tools. It’s software, and this software gives you tremendous control over your CPU, and if you just click on random things, you can mess things up. In this lesson, we’re going to look at one thing that is bolted on, and it’s very secure.
- Two of the most popular applications that users use are Intel XTU and Throttlestop. Both are free, both are good, but for beginners I would recommend XTU because it has all the basic components you really need.
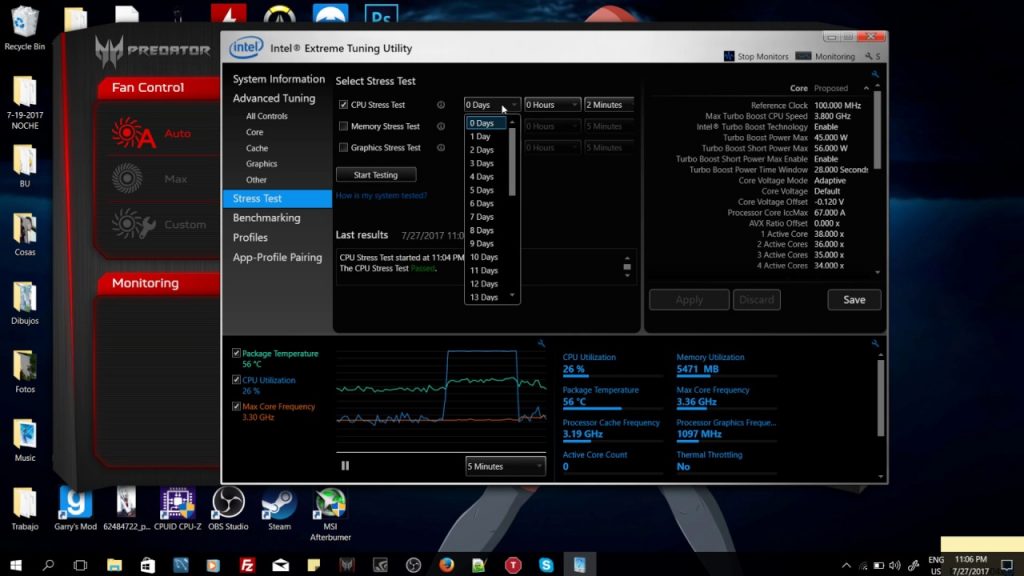
- This is XTU at first charge. The complex numbers sound crazy, but you can ignore most of them.
- First, set up your graphical monitor to display 30 minutes of data. Test your CPU on it without any adjustments to see what numbers you get.
- Here is an XPS 15 9560 laptop running KB Lake 7700 HQ. During the stress test, the processor was running pretty busy, with occasional swings and temperature ups and downs as the fans turn on and off. The highest temperature was 88 degrees and the coldest was about 76 degrees.
- The right way to properly strip now is to lower the voltage, do a stress test, then lower the voltage again and start over. Basically the CPU is starving more and more.
If you don’t want Throttlestop to open manually every time you turn it on, you can choose to open it at Windows startup. For more information, see. In our guide to using the Windows Task Scheduler.
Undervolting using XTU
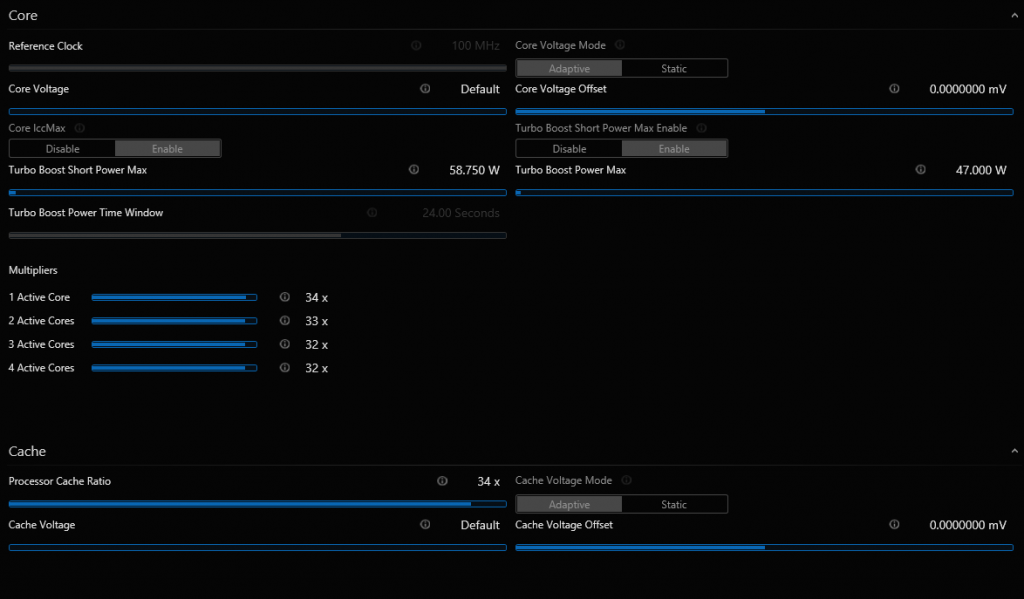
- Go to advanced settings and click the core voltage offset on the Core tab (2). You want to scroll to zero to display negative numbers. Remember, we live here, so you want to select negative voltage and make changes.
- Running from a reduced voltage of 50 millivolts means 0.050 volts. And since it is alive, the value is -0.050 volts.
- Stress tests reach a maximum of 84 degrees. Make sure that the system is still completely stable. We get full clock speed, which shows that this is a step in the right direction.
- If you go one step higher, you can lower the voltage by reducing it by 120 millivolts or -0.120 volts. I’m cheating here because I know that’s almost the limit for this particular processor. You have to gradually reduce it and test it a little bit, but for speed I’m going to turn this knob by ten.
- With this lowered voltage we get even lower temperatures, 77 degrees at most during the stress test and when you activate the diagram, so the original voltage is down a good 10 or 11 degrees unchanged.
- If you drop my voltage to -130 millivolts, it freezes and may even turn blue. If it does, then you have reached your voltage drop limit. At this point, restart the computer, go back to XTU, and go back to the last operating voltage.
- To really test for stability, you’ll want to run something like Prime95 overnight to make sure everything is okay. If it doesn’t last all night, increase the blood pressure.
- All processors are different, so I can’t tell you exactly where to start. However, I would recommend looking into your particular processor or laptop and seeing what other users have been able to do with that hardware, and just using it as a quick start.
Using this method, I’ve lowered my CPU gaming temperature from almost 90° C to a less alarming 70° C to 75° C. That’s about as much as you can affect the CPU temperature in Windows.
If you are still having problems, you need to open up your computer and apply thermal paste to the CPU or remove dust.
Expert Tip: This repair tool scans the repositories and replaces corrupt or missing files if none of these methods have worked. It works well in most cases where the problem is due to system corruption. This tool will also optimize your system to maximize performance. It can be downloaded by Clicking Here
