Updated February 2025: Stop getting error messages and slow down your system with our optimization tool. Get it now at this link
- Download and install the repair tool here.
- Let it scan your computer.
- The tool will then repair your computer.
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a standard application protocol used by Windows Server Active Directory (AD) to maintain directory services. Client devices and applications authenticate to the AD using LDAP “binding” operations. Simple LDAP binding involves sending user credentials in plain text over the network. This means that there is no encryption of the user name and password. Although the DA supports simple binding, it is not a recommended approach.
Applications that use simple LDAP bindings should be upgraded to use Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) bindings that support characters and seals (verification/integrity and encryption) instead. Applications that cannot be upgraded can use LDAP over TLS, sometimes called LDAPS, but implementation and maintenance is more complex.
The good news is that all currently supported versions of Windows negotiate signed LDAP connections by default. However, Active Directory accepts simple LDAP connections unless LDAP signature is set to “required”. If LDAP is set to “required” in a domain, simple LDAP bindings will fail. So, if you want to make sure that simple LDAP bindings are not used, you must configure AD to require LDAP signature. As with any security change, before you allow a domain to use LDAP signing, you must perform a thorough test to ensure that you do not have applications that rely on simple LDAP bindings.
LDAP Signature Levels
There are three levels that SASL can use to sign data in Active Directory
- Not required (level 0)
- Sign if both parties are capable (level 1)
- Always sign (level 2)
On a domain controller, the required signature level is defined in the parameter HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ System \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ NTDS \ under the value LdapServerIntegrity (REG_DWORD) in the registry key. The value can be overridden by the Group Policy under Computer Configuration \ Windows Settings \ Local Policies \ Security Options under Domain Controller: Ldap Server Signing Requirements.
Microsoft recommends that administrators make the hardening changes described in ADV190023 by increasing the value of LdapServerIntegrity from 1 to 2.
Client
The client signature level is defined in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ System \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ LDAP registry key under the value LdapClientIntegrity. The value can be changed using the group policy under Computer Configuration \ Windows Settings \ Local Policies \ Security Options under Network Security: LDAP Client Signing Requirements.
LDAP signing support has been added to Windows 7 (Service Pack 1) and Windows Server 2008 R2. If both the client and server support it and have a value of 1 or greater, they will negotiate and use it.
Some older PowerShell or Visual Basic scripts may attempt to open an LDAP connection with plain text credentials if the script does not request the LDAP signature. See Identifying plain text LDAP links to your DCs.
Enabling LDAP Signing Using Group Policy
February 2025 Update:
You can now prevent PC problems by using this tool, such as protecting you against file loss and malware. Additionally, it is a great way to optimize your computer for maximum performance. The program fixes common errors that might occur on Windows systems with ease - no need for hours of troubleshooting when you have the perfect solution at your fingertips:
- Step 1 : Download PC Repair & Optimizer Tool (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista – Microsoft Gold Certified).
- Step 2 : Click “Start Scan” to find Windows registry issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Step 3 : Click “Repair All” to fix all issues.
How to specify the LDAP server signature requirement
- Select Start > Run, type mmc.exe, and select OK.
- Select File > Add/Remove Snapshot, select Group Policy Management Editor, and select Add.
- Select Select Group Policy Object > Browse.
- In the Find Group Policy Object dialog box, in the Domains, OR and Related Group Policy Objects area, select Default Domain Controller Policy and select OK.
- Select Finish.
- Select OK.
- Select Default Domain Controller Policy > Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies, and select Security Options.
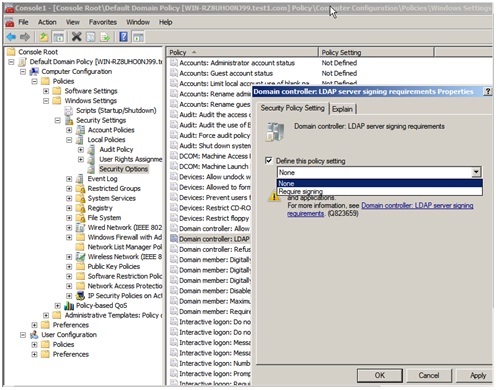
- Right-click Domain Controller: LDAP Server Signing Requirements and select Properties.
- On the Domain Controller: LDAP Server Signing Requirements properties, enable this policy setting, select Signing requirements from the Define this policy setting list, and select OK.
- In the Confirm Changing Settings dialog box, select Yes.
To define the customer’s LDAP signature request using Local Group Policy
Select Start > Run, type mmc.exe, and select OK.
Select File > Add/Remove Snapshot.
In the Add or Remove Snapshots dialog box, select the Group Policy Object Editor, and then select Add.
Choose Finish.
Choose OK.
Select Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies, and select Security Options.
Right-click Network security: LDAP client signing requirements, and select Properties.
Under Network Security: LDAP Client Signing Requirements Properties, select Signing Requirements from the list, and select OK.
In the Confirm Settings Change dialog box, select Yes.
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/935834/how-to-enable-ldap-signing-in-windows-server
Expert Tip: This repair tool scans the repositories and replaces corrupt or missing files if none of these methods have worked. It works well in most cases where the problem is due to system corruption. This tool will also optimize your system to maximize performance. It can be downloaded by Clicking Here
